Less Known Facts About Muslims in India

Two concerns dominate discussions of Indian Muslims: that they lag behind other groups due to discrimination and cultural factors, and that gender gaps among Muslims are likely substantially wider because of cultural reasons. If true, both should be visible in development indicators. Let’s look at the facts.
- Infant Mortality: According to Vaclav Smil (PDF), one of Bill Gates' favorite authors, “Infant mortality is an excellent proxy for a wide range of conditions including income, quality of housing, nutrition, education, and investment in health care.” Indian Muslims have long enjoyed an advantage over Hindus (see here and here).
- Stunted, Wasted, and Underweight Children < 5: The percentage of stunted, wasted, and underweight children in India is horrifying (see NHFS 2019-2021; pg. 423). But the differences between Muslim and Hindu children are at worst about a percentage point.
| Measure | Hindu | Muslim |
|---|---|---|
| Stunted (height-for-age < -2 SD) | 35.5% | 36.8% |
| Wasted (weight-for-height < -2 SD) | 19.3% | 20.0% |
| Underweight (weight-for-age < -2 SD) | 32.3% | 32.8% |
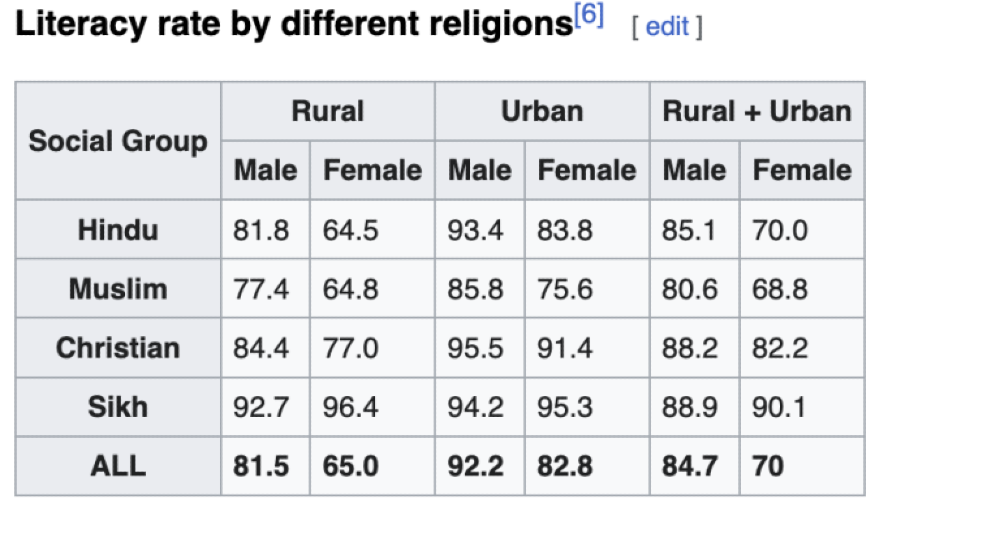
- Literacy: Rural Muslim women are slightly more literate than rural Hindu women. The male-female literacy gap is also narrower among Muslims than Hindus, in both cities and villages. (Note how pleasing the numbers are among Sikhs.)
Note: On median number of years in school, the differences between Hindu and Muslim men are sharper but differences between women are small (see here).
- Household Expenditure: The Muslim/Hindu household expenditure ratio across rural India is 110 (see here). After adjusting for household size, it drops to 97. In no state except Delhi (which has a tiny rural population) is the ratio lower than 83, and in 15 out of 22 states (as of 2007), the Muslim/Hindu ratio is over 100. There is significant regional variation. Muslims in rural Kerala have a higher average household expenditure than the mean household expenditure among rural Hindus in any state. The urban Muslim/Hindu expenditure ratios look starker, but the mean is 87. None of this accounts for the fact that Muslims are, on average, younger than Hindus.
- Clean Fuel. The use of unclean fuel nearly halved between NHFS-4 and NFHS-5 for both Hindus and Muslims. Among Hindus, it fell from 82.76% to 41.70%, while among Muslims, it fell from 86.06% to 42.66% (see here). (This kind of converge across groups holds across many of the variables. See TFR and polygyny, for instance.)
- Share of Population and TFR: The share of Hindus as a percentage of the population has declined by nearly 8% over the decades. Compare that to India’s neighbors, especially East Pakistan/Bangladesh, but also Burma (see here). One metric correlated with development is TFR (Total Fertility Rate). In the last 27 years, the TFR among Hindus has declined from 3.3 to 1.9, while among Muslims, it has declined from 4.4 to 2.4 (see here).
- Polygyny: IIPS reports that 1.9% of currently married Muslim women report their husband has another wife, versus 1.3% for Hindus (see here). (Note: In NHFS-3, the difference was 1 percentage point.)
- Marriage < 18. One in five Indian women aged 20–24 married before 18, half the rate of two decades ago. Hindu and Muslim rates are virtually identical (see here). If we account for some of the confounding variables, the rate among Muslims is about 3.5 percentage points lower (see here).
- Percentage of 15–49 Women That ...
| Hindu women | Muslim women | |
|---|---|---|
| Own a House (alone or jointly) | 42.6% | 38.5% |
| Own Land (alone or jointly) | 32.6% | 28.7% |
| Have a mobile phone they themselves use | 53.8% | 51.3% |
| Have a bank account | 79.3% | 73.4% |
Hindu women edge out Muslim women on each measure—house ownership, land ownership, mobile phones, bank accounts—but the gaps are narrow, ranging from 2.5 to 6 percentage points (see here).